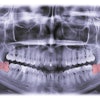
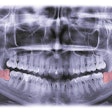
Cellceutix has filed an application with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requesting orphan drug designation for its antibiotic Brilacidin-OM as a drug candidate for preventing radiation or chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients
Brilacidin-OM is a defensin mimetic that has antibacterial, antibiofilm and anti-inflammatory properties, according to the company.
Currently, Cellceutix is planning a phase II trial of brilacidin-OM to meet an area of unmet medical need for cancer patients who suffer from the condition that is a common, and often debilitating, side effect of chemotherapy and radiology therapy.
At the 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, the company reported that Brilacidin reduced the occurrence of severe ulcerative oral mucositis in animal models by more than 94% compared with placebo.
Orphan drug designation is intended to facilitate drug development for drugs that target conditions affecting fewer than 200,000 patients in the U.S. annually, while providing a significant therapeutic advantage over existing therapies. The designation carries several benefits, including fee reductions, assistance in study design from the FDA, potential for expedited drug development, eligibility for drug grants, tax incentives, and extended market exclusivity.